Publicly reporting ESG data effectively is a key part of building trust and transparency. By sharing this data, companies showcase their commitment to sustainability and highlight their progress toward climate change goals. Let’s dive into the difference between ESG data and regulatory reporting.
What is the Difference Between ESG Data and ESG Reporting?
While they go hand-in-hand, ESG data and ESG reporting serve different research purposes:
-
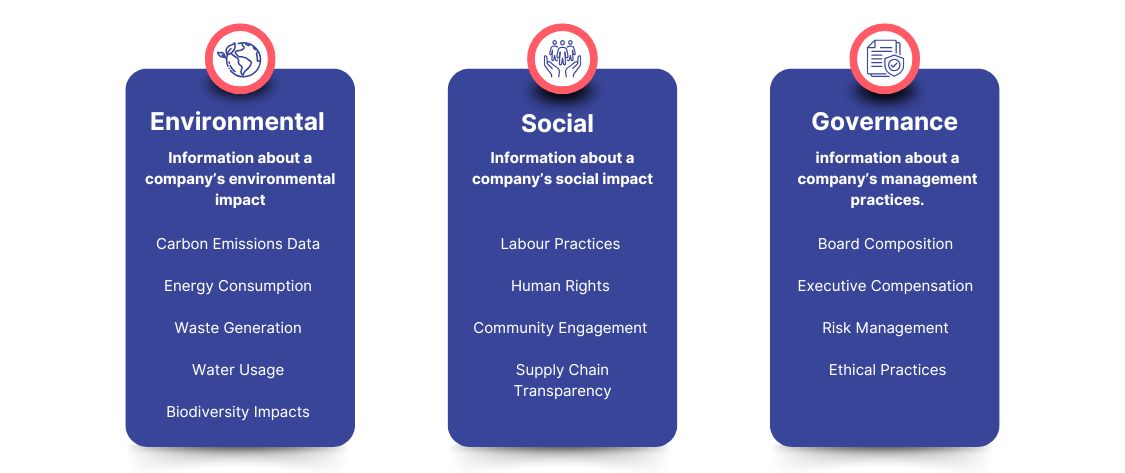
ESG Data: This is the raw information—such as greenhouse gas emissions, employee diversity statistics, and energy use—that tracks a company’s ESG performance.
-
ESG Reporting: This is the process of communicating ESG data in a structured, understandable way for stakeholders. ESG reporting translates data into a story, showing how the company is meeting its goals, where it’s making progress, and areas for improvement.
In short, ESG data is the raw material, while ESG reporting is the polished, accessible presentation that stakeholders rely on for insights.
ESG Reporting Requirements and Regulations
ESG reporting requirements vary depending on a company’s industry, location, and size. While some organizations voluntarily disclose their ESG performance, others are required to meet specific regulations that are becoming increasingly stringent:
-
Country and Industry Variations: Different regions and sectors have unique ESG reporting standards. For instance, the EU has stricter regulations than some other regions, requiring large companies to disclose specific information about their environmental and social impact.
-
Increased Stringency: Globally, governments and regulatory bodies are raising the bar on ESG reporting. Companies are being called to provide more accurate, timely, and transparent information about their impact on the environment and society.
Best Practices for ESG Reporting and Disclosure
High-quality ESG reporting requires clear, accurate, and verified information. Here are some best practices to ensure your reports are informative and trustworthy:
-
Use Clear and Concise Language: It’s important to communicate ESG data in straightforward language that all stakeholders can understand. Avoid jargon where possible and focus on explaining metrics and results in a way that’s accessible to a broad audience.
-
Use Data Visualization and Reporting Techniques: Visual elements like graphs, charts, and tables can make complex data much easier to interpret. Visualization helps stakeholders see patterns and trends at a glance, which is especially helpful when dealing with large amounts of data.
-
Use Third-Party Assurance and Verification: To enhance credibility, consider having your ESG data verified by an independent third party. Assurance services validate the accuracy and reliability of your data, building trust with stakeholders and reinforcing your commitment to transparency.
Incorporating these best practices into your ESG reporting process helps you craft a report that not only meets your own regulatory and reporting requirements but also resonates with stakeholders. Thoughtful ESG reporting turns raw data into a compelling narrative that demonstrates your company’s dedication to sustainability.
Accessing ESG Data