FAQs
What are examples of distributed energy?
Common examples of distributed energy include solar panels, wind turbines, combined heat and power (CHP) systems, battery storage, and fuel cells. These technologies generate electricity locally, reducing reliance on centralized generation and improving efficiency.
What are examples of DERs?
Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) include solar PV systems, energy storage batteries, electric vehicles (EVs), natural gas-fueled microturbines, and CHP units that generate both heat and power. They are often installed on rooftops, in industrial facilities, and within microgrids.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of distributed energy resources?
Advantages: DERs reduce transmission losses, improve energy security, lower environmental impacts, and offer cost-effective solutions for businesses. They enable energy storage, support renewable integration, and provide backup power during outages.
Disadvantages: Challenges include high upfront costs, the need for advanced energy management systems, and intermittent supply from renewable sources like solar and wind. Integration into existing grids also requires technical expertise.
Why should energy resources be distributed?
Distributing energy resources improves resilience, reduces transmission losses, and allows electricity to be generated closer to where it’s consumed. This enhances grid flexibility, lowers dependence on fossil fuels like natural gas and diesel fuel, and supports the development of smart grids and local energy markets.
What is meant by distributed energy?
Distributed energy refers to small-scale power generation systems located close to where energy is consumed. These systems, such as solar panels, CHP units, and battery storage, reduce the need for long-distance electricity transmission and improve overall system efficiency.
What is the meaning of energy distribution?
Energy distribution is the process of delivering electricity from generation sources—both centralized and distributed—to consumers. Distribution networks connect power systems with homes, businesses, and industries, ensuring a stable energy supply for heating, cooling, and daily operations.
What is distribution system energy?
Distribution system energy is the electricity delivered through local grids to consumers. It includes energy generated from centralized power plants and distributed generation sources like DER units. Advanced energy management ensures efficient operation and minimizes transmission losses in these systems.
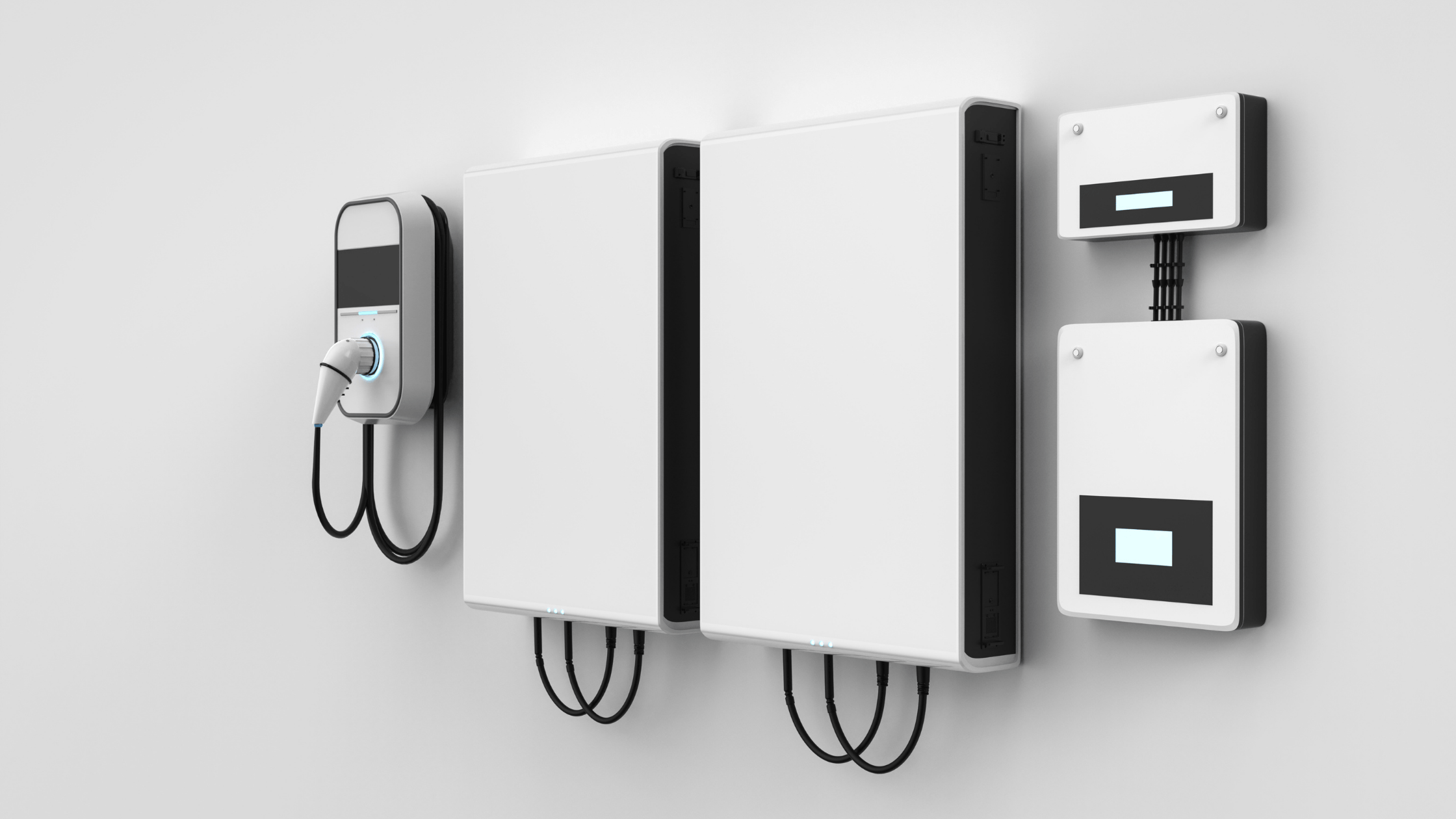
What is a distributed power system?
A distributed power system is a network of connected DER units that generate and store electricity near the point of use. These systems are supported by energy storage solutions, smart grids, and technologies like combined heat and power (CHP) to ensure reliable and flexible power supply for homes, businesses, and industries.